In this article, we explain to you Linux vi commands and Implement them.
Theory and Output:
- The vi editor (short for a visual editor) is text editor which is available on almost all Unix/Linux systems
- vi has no menus but instead uses combinations of keystrokes in order to accomplish commands.
- you can use vi editors to edit(add, change, and delete text) an existing file or to create a new file from scratch. You can also use this editor to just read a text file
The UNIX vi-editor is a full-screen editor and has two modes of operation:
- Command mode: This mode enables you to perform administrative tasks such as saving files, executing commands, moving the cursor, cutting and pasting lines or words, and searching and replacing. In this mode, whatever you type is interpreted as a command
- Insert mode: This mode enables you to insert text into the file. Everything that’s typed in this mode is interpreted as input and finally, it is put in the file.
- By default vi is in command mode.
Linux vi commands and Implement them
Refer one by one command to better understand
The Syntax for creating (if not created before) and opening files in vi-editor:
$ vi <file-name>
1– i command:- This command is used to insert data in the file/used to go in insert mode.
After pressing (i) it will go into insert mode and we can write some content inside the file.

Also read: – How To Recover Deleted Files, Photos, Videos, Documents
2- Esc command: This command is used to escape out from the insert mode and come back to the command mode.
Note

3-a command:- This command is used to append the more data/go back to the insert mode.
Appending new data.

4-A command:- This command is also used for inserting a new data but at the end of line/goes into insert mode
This image shows cursor is in the midway.

5-u command: This command is used for undo the last change.(we have added rollno here)
That last change

6-o command: This command open a new line/goes into insert mode.
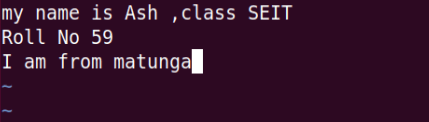
7- O command:- This command before open a new line/goes into insert mode.

8–dd command: This command is used to delete one single line.
One line get deleted.

Suggested: – How to install Ubuntu on Virtual box for windows.
9-D command: This command delete the content of the line after cursor
You can see delete command work after m i.e. M Matunga.
. You can delete one by one word also


10- C command:- This command delete the content of the line after cursor and insert new text.

11- dw command: – This command delete s a single word.
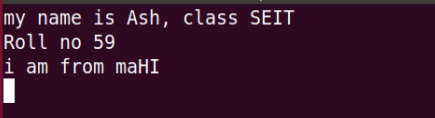
12- cw command: – This command changes the word.

13- x command– These commands at cursor.

14-r command: This command replace s the char.

15-R command: This command overwrites char from cursor onwards.

16-s command: This command substitute one char under cursor and continue to inserting from that position.
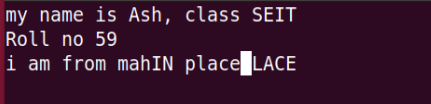
17-S command: This command substitute entire line and begin to insert at the beginning of the line.

18-~ command: This command change char of each case.

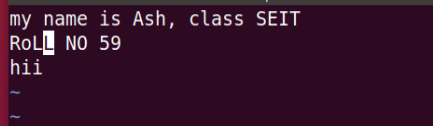
19-k command: Move cursor up in command mode.
Before k mode:
After k command:


20-j command: Move cursor down in command mode
Before:


21-h command: This command move cursor left in command mode
Before:
After h command i.e left:


22-l command: This command move cursor in right direction.
Before:
After h command i.e right:

23- w command : This command saves the file but keep it open
24-shift+zz and : wq command: These both commands save the file and quit.
:q command: This command quit without saving.




Hello there, You have done a fantastic job. I’ll certainly digg it and for my part recommend to my friends. I’m sure they’ll be benefited from this site.|