Before the implementation of Linked List, we first learn what is LL, Operation, and Types.
Implementation of Linked List
Q. What is a linked list?
ANS.: Collection of a node representing data and a next pointer pointing to the next node.
Q. Operations performed on a linked list?
ANS.: Creation, insertion, deletion, traversing, searching, concatenation, split, reversing and display.
Q. Advantages of a linked list?
ANS.: Dynamic, memory-efficient & insertion and deletion is faster.
Q. Types of the Linked list?
ANS.: Linear, Circular & Doubly.
Also, you can use c compiler to compile a program.
Graphical Representation.
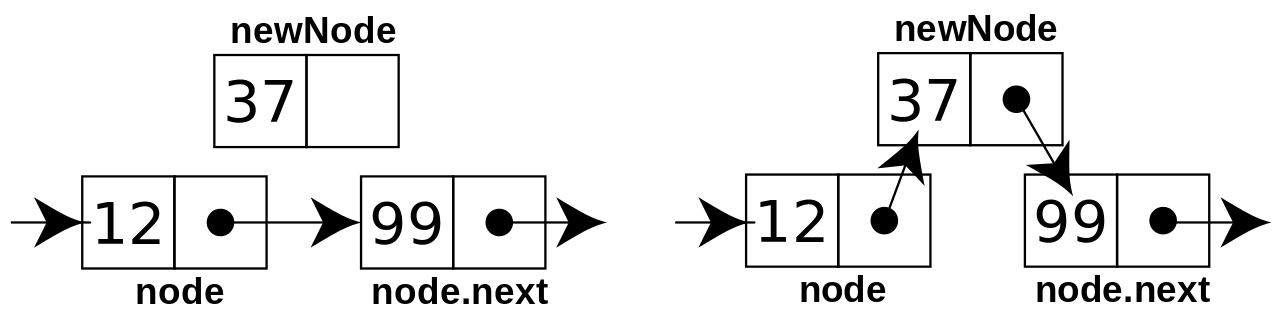
Program.
Source code.
//stack using linked list
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
struct node
{
int data;
struct node * addr;
};
struct node * start;
void ins(int);
void del(int);void disp();
int main()
{
printf("-insert-");
ins(10);
ins(20);
ins(15);
ins(30);
printf("\n-del-20");
del(20);
printf("\n-del-15");
del(15);
}
void ins(int val)
{
struct node * temp,*curr,*prev ;
temp=(struct node *) malloc (sizeof (struct node));
temp -> data=val;
temp-> addr=NULL;
if(start==NULL)
{
start=temp;
}
else
{
curr =start;
prev = NULL;
while(curr!=NULL && curr->data<val)
{
prev= curr;
curr=curr->addr;
}
if(prev==NULL)
{
start = temp;
}
else
{
prev->addr=temp;
}
temp->addr=curr;
}
disp();
}
void disp()
{
struct node * i=start;
printf("\nstack: ");
while(i!=NULL)
{
printf("%d ",i->data);
i=i->addr;
}
}
void del(int x)
{
struct node *curr, *prev;
curr = start;
prev = start;
while(curr-> data!=x && curr!=NULL)
{
prev = curr;
curr = curr->addr;
}
if(curr == NULL)
printf("\nError : %d\n not found\n",x);
else if(curr == start)
start = curr->addr;
else
prev->addr = curr->addr;
disp();
}Output.
-insert-
stack: 10
stack: 10 20
stack: 10 15 20
stack: 10 15 20 30
-del- 20
stack: 10 15 30
-del- 15
stack: 10 30
Also View – Stack using
Also View – Queue using a linked lists.
Also View- Write a java program to create a window using swing.


Incredible points. Sound arguments. Keep up the great work.